Software updates are great because they keep installations secure and add new functionality. Moving from one Debian version to the next, however, is sometimes a bit painful for projects that modify system configuration files. My VPN-Wifi-Pi project that uses a Raspberry Pi as a Wifi Access Point and an OpenVPN tunnel to a VPN server for secure Wifi access in hotels and other places is unfortunately no exception.
Author: Martin
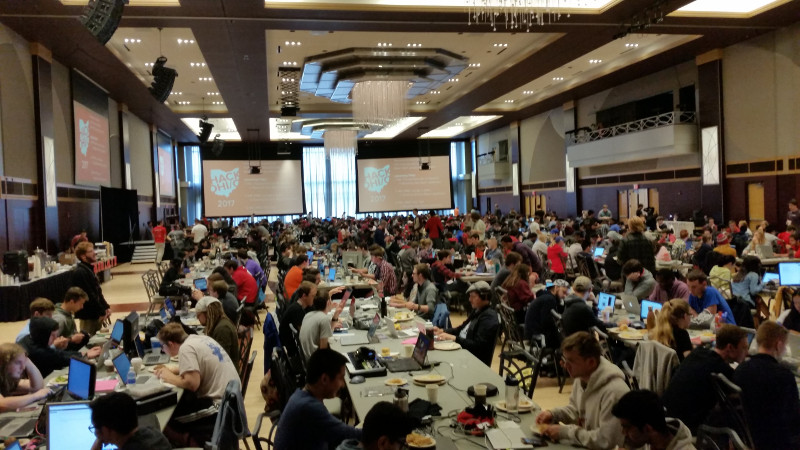
Wi-Fi For 750 Hackathon Participants
The 28 GHz 5G Frontier
5G is many things to different people. For most, 5G is about more network capacity and faster speeds for Internet access. The main challenge for this goal is that there is little spectrum still available below 6 GHz, a frequency that is generally seen as the limit for the current air interface technologies around. So 5G below 6 GHz brings only few benefits for the broadband Internet use case, it could easily be done with LTE as well. Ultimately, to get to higher speeds and more network capacity, higher frequency bands have to be tapped. The problem here is that with conventional technologies, communication range is severely limited.
Eduroam Configuration App for Android
 Setting up Eduroam on a PC securely including certificate checking during authentication to prevent password theft is quite a bit of a challenge but not impossible. On Android, things are even more difficult and it’s a bit strange that many universities are showing how to configure Eduroam manually on their help pages rather than linking to the Eduroam Configuration Assistant Tool (eduroamCAT) web page that makes things a lot easier.
Setting up Eduroam on a PC securely including certificate checking during authentication to prevent password theft is quite a bit of a challenge but not impossible. On Android, things are even more difficult and it’s a bit strange that many universities are showing how to configure Eduroam manually on their help pages rather than linking to the Eduroam Configuration Assistant Tool (eduroamCAT) web page that makes things a lot easier.
Small Cell Network Sharing As A Way Forward To Network Densification?
Recently, I’ve been thinking a bit how network densification will look like once the capacity of macro cells is no longer sufficient to satisfy demand. As statistics keep telling us, a significant part of cellular data traffic is not generated outdoors but actually indoors. When densifying the network its unlikely that this would work well from the outside, densification has to be done from within buildings.
Continue reading Small Cell Network Sharing As A Way Forward To Network Densification?
The Mouse – An Endangered Species?
 While traveling, I recently spent some time on a University campus in the US and sat in the Library reading room for a few hours. When I observed the students there for a while I noticed that none, not even a single one of them used a mouse with their computers. Instead, they were all using the touchpad of their notebooks while I was the only one in the reading room who actually had a mouse at the side of this computer.
While traveling, I recently spent some time on a University campus in the US and sat in the Library reading room for a few hours. When I observed the students there for a while I noticed that none, not even a single one of them used a mouse with their computers. Instead, they were all using the touchpad of their notebooks while I was the only one in the reading room who actually had a mouse at the side of this computer.
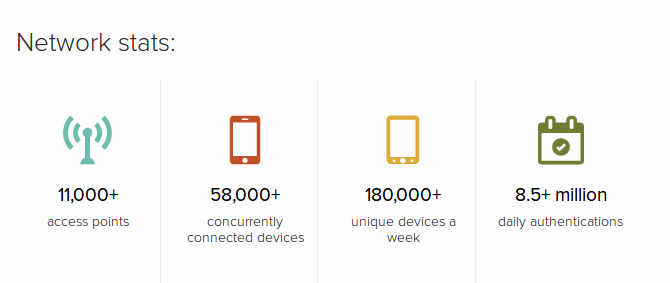
11.000 Wi-Fi Access Points At Ohio State University
When I was recently at the Ohio State University for a few days I noticed the following interesting statistics about their Wi-Fi network:
Quite impressive numbers, especially when setting them into perspective:
Continue reading 11.000 Wi-Fi Access Points At Ohio State University
From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G – My Latest Book Is Now Available!
 Time flies and it’s already 3 years since the previous edition of my book became available. Time for an update and I’ve worked hard over the course of the past 12 months to ensure my introduction book on wireless networks continues to reflect the latest state of how the technology is deployed and functions in practice. A lot of things have happened in the past three years so I had to adapt the title a bit and the third edition is now called ‘From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G‘! So what’s new?
Time flies and it’s already 3 years since the previous edition of my book became available. Time for an update and I’ve worked hard over the course of the past 12 months to ensure my introduction book on wireless networks continues to reflect the latest state of how the technology is deployed and functions in practice. A lot of things have happened in the past three years so I had to adapt the title a bit and the third edition is now called ‘From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G‘! So what’s new?
Continue reading From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G – My Latest Book Is Now Available!
Tales From a 3GPP Meeting
I recently came across this interesting post by Michael Thelander over at RCR Wireless in which he describes how 3GPP meetings and the people attending ‘tick’ from his point of view. Regularly attending industry meetings around the world on a quarterly meeting myself I’m glad that these meetings are a tad more relaxed in most aspects than what Michael describes in his post. I’ve heard similar stories of 3GPP meetings from other people in the past so I don’t think he’s exaggerating.
One thing he doesn’t mention is how well Internet connectivity works when hundreds of people attend such meetings. From what I’ve heard, 3GPP meeting organizers take special care to select venues with high speed Internet connectivity (and I don’t mean a DSL line with a few Mbit/s) and bring their own kit to manage the traffic. Still, I’ve heard people saying that often, Internet connectivity is a challenge during meeting weeks. Let’s see Michael’s post was titled ‘part 1’, so perhaps he’ll mention something on this in future posts.
How Many GB Do €30 Buy You? – And Other Interesting Stats
It is actually quite shocking to see a comparison of how much mobile data €30 buys you in different countries in Europe. Let’s take a look at two examples: In Germany, according to the statistics of Rewheel and my own experience, €30 buys you around 6 GB with the cheapest network operator and far less with other network operators. On the other end of the scale is Finland where less than €30/month gets you a ‘all you can eat’ flatrate subscription!
Continue reading How Many GB Do €30 Buy You? – And Other Interesting Stats