Last week I reported on my new Wi-Spy analyzer that has gripped my imagination and is since scanning the ISM band used by Wifi, Bluetooth and other radio systems wherever I go. Today I’ve got a couple of additional traces which I think are spectacular enough to show around.
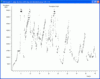
The first picture on the left shows how the ISM band looks like in my neighborhood. There’s one Access Point broadcasting away on channel 1. On channel 2 there are another two access points and probably a third one which is farther away and thus it’s amplitude is much lower than those of the other two. My own access point operates on channel 11 and sent a lot of data to my notebook when the trace was taken. Hence the access point emissions are shown in red. The notebook doesn’t send a lot of data but has a higher amplitude since the antenna is closer to the Wi-Spy probe. Since there is a notebook with an ‘old’ 802.11b network card in the network both the access point and my notebook send ‘Clear To Send’ packets with direct spread (DSSS) modulation. This shows quite nicely in the trace with the two side lobes to the left and right of the high main arch produced by the receiving notebook. The data packets itself are sent with 802.11g OFDM modulation which produces a much flatter main arch. The red space in the trace is actually a mixture of DSSS and OFDM modulation. Look closer and you will also see an access point transmitting on channel 9.
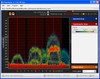
The second image on the left shows what happens when a Wifi card runs wild. Before I ran the test I remembered that I had a broken 802.11g network card which used to always work quite well for a couple of minutes before loosing the network. As can be seen in the figure, loosing the network actually means going completely wild. It looks like it completely looses modulation and after a short stint in the original band where it used to send and receive it moves down the bottom of the ISM band with the two main archs at 2410 and 2420 MHz. The peaks on the side are probably the side lobes. Looks like the wifi card is blasting away on full power throughout the band and I am sure it wracks havoc on any transmissions within reach… Looks like the wifi card is ready for the scrap yard.
So much for today. For more traces take a look at my previous entry, at the trace library over at Metageek either here or here.