In the previous post I've described my first experience with an Acer Aspire One D250 netbook together with eeeBuntu (based on Ubuntu 9.04 Jauntry). I was quite impressed of how easy it was for the most part to get going. In this part I will look at how to get eeeBuntu working witch a 3G USB dongle and a mobile phone.
Easy Installation and Use
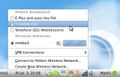 EeeBuntu detected both my Huawei E220 3G dongle and my Nokia N95 as wireless modems straight away, no configuration necessary. The first time they are connected, a configuration menu automatically appears which contains a pretty extensive network operator and APN settings list. After selecting a country and network, a profile is automatically created and added to the network list in the taskbar. Strangely enough, the menu entry did not appear straight away in all cases, sometimes a reboot was necessary when adding an new profile. In case the operator is not in the database, it’s possible to just select one of the operators and then edit the configuration by hand.
EeeBuntu detected both my Huawei E220 3G dongle and my Nokia N95 as wireless modems straight away, no configuration necessary. The first time they are connected, a configuration menu automatically appears which contains a pretty extensive network operator and APN settings list. After selecting a country and network, a profile is automatically created and added to the network list in the taskbar. Strangely enough, the menu entry did not appear straight away in all cases, sometimes a reboot was necessary when adding an new profile. In case the operator is not in the database, it’s possible to just select one of the operators and then edit the configuration by hand.
PIN protection Issue
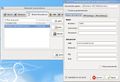 Most of my SIM cards are not PIN protected so clicking on the new network profile entry connects to the network very quickly. With some of my SIMs, however, the PIN can’t be deactivated so the 3G dongle requires the PIN before launching the connection. While this worked pretty well the first day, I started to get problems since then and the behavior became pretty erratic. In the end, I wrote a shell script to send the PIN to the modem before using one of the 3G profiles.
Most of my SIM cards are not PIN protected so clicking on the new network profile entry connects to the network very quickly. With some of my SIMs, however, the PIN can’t be deactivated so the 3G dongle requires the PIN before launching the connection. While this worked pretty well the first day, I started to get problems since then and the behavior became pretty erratic. In the end, I wrote a shell script to send the PIN to the modem before using one of the 3G profiles.
Disconnecting and Status Information Missing
Disconnecting from the network also worked well via the network menu during my experiments the first day. Since then, however, for reasons unknown, clicking on “disconnect” has no effect, not with the E220 and also not with the N95. Unplugging the dongle or the mobile cuts the connection but brings further trouble. In many cases plugging the E220 back into the USB port has no effect and eeeBuntu needs to be rebooted. In Windows on the same machine, unplugging and plugging the dongle back in works well, so it’s not a hardware issue. With the N95 unplugging and plugging in again works in most cases.
Another thing that bugs me is that I have no means of seeing signal strength or to lock the 3G dongle to a certain operator or network technology as I can easily do in the launcher program provided for Windows. Too bad as this is a very handy functionality in some situations!
Summary
While the basic implementation for 3G connectivity works well, it is unfortunately a bit unreliable in eeeBuntu version 3. While I can maneuver around the issues, a normal user is likely to get frustrated.