Teltarif recently reported that one of the mobile network operators in Germany has pledged that they will blanket Germany with LTE by 2015 by using 10.000 LTE base stations. I wonder if that number is correct, however, as according to their Wikipedia entry they currently have 20.000 GSM base stations and 13.000 UMTS station to cover the nation. So either the wrong number of base stations has been reported, somebody is delusional or it's a marketing gag!? 2015 is not far away so we'll see soon.
Owncloud 6 Months Later – A Status Report
Half a year ago two things came together that reconciled me with cloud computing: A Raspberry Pi, an inexpensive Linux computer than I can run 24/7 at home as it requires very little power and Owncloud, a piece of open source software that lets me, as its name says, run my own cloud services at home. Not trusting web companies to keep my private data safe even before the recent PRISM revelations I could not export my private data to web based companies. So until then, even though it would have been convenient, I didn't synchronize my calendars and address books on different devices and also did not use cloud storage for exchanging files between different devices and to make them available to others. Obviously when I got things working for the first time I was overjoyed. But how has the setup fared in the past 6 months as routine has set in?
Contacts
In short, it has performed beyond my expectations. Address book synchronization between my Android based mobile devices and Owncloud works like a charm. The only glitch I found so far is that when I rename a contact via the Web interface the change is not propagated to my mobiles. If I do the same on a mobile device, however, the change is properly synchronized. Changes in all other fields are synchronized just fine both ways. Since names of contacts usually change very little that's something that can easily be lived with.
Another thing, due to the limited speed of the Raspi is that it takes a while for the pictures of my contacts to show up in the web interface, even for those contacts that I don't have any pictures and thus get a neutral logo. This has the effect that when I just want to quickly go to my contacts on the PC and then change something it takes a bit for the dialog box that pops-up with the contact's information to become editable. This is not a bug but rather a bit of a usability issue and again not something that stands in the way of an otherwise great usability experience.
Calendar
Calendar synchronization has become even more important to me than address book synchronization across Thunderbird/Lightning on the PC and Android based devices. The Owncloud calendar can be used in Thunderbird with or without a local copy. Over time I noticed that when keeping a local copy, Thunderbird refuses at some point to let me delete some entries while I can delete others just fine. I haven't found a pattern in the behavior but it's not a problem in practice as the online mode that just caches information in Thunderbird for times when a connection to the server is not available works without a flaw. The only downside of online mode is that for adding, removing or changing an entry, Thunderbird needs to have a connection to the Owncloud server. Again, only a problem when I'm not connected, which is pretty much only when I'm on a plane. And even then, I can modify the calendar on my mobile device and changes are synchronized back to Owncloud and Thunderbird as soon as connectivity is reestablished.
File Sharing
I use Owncloud's file storage for sharing files between different devices of my own and also to share files that are too big to be included in emails. Individual files or complete directories can be shared with others without the need for an Owncloud account for the person on my server by generating a link that can simply be clicked. Again, this works great in practice.
A feature requests for the future would be for Owncloud show pictures in externally shared directories with the same gallery option as it does when I view them myself or if I share them with another Owncloud user on my sever. Also, when sharing only a single file the download button should be more in the center of the web browser rather than on the top right for users to find it more easily. Nobody's complained to me about it but I find the layout a bit odd. And finally, I'd like to see an option for external sharing that does not only give me a URL that can be used in my home network but in addition a URL that can be used externally. Today I copy/paste the URL to an email and then replace the beginning of the link with my externally visible URL and a different TCP port number. Not a problem for me but normal users struggle a bit with this.
Summary
Yes, I know, there are a lot of other applications for Owncloud but those three are the ones I use on a daily basis. I can't say this often enough, the combination of a Raspi and Owncloud has been a real game changer for me as I now enjoy the benefits of cloud services without the need for putting my private data out of my zone of trust.
Osmand: Bye Bye Nokia Maps – Bye Bye Google Maps
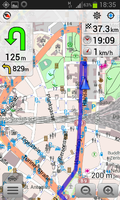 Due to Nokia's decision to back away from freedom and open source I was forced over the past year or so to rely on a two device strategy while traveling as there were two crucial applications missing for me on Android so far: A decent camera and offline maps + navigation functionality. While the camera issue has improved significantly in the past year I was still hanging on to Nokia Maps and its offline capabilities as Android's Google maps was just too expensive to use abroad and leaked too much of my location information to Google. But now, things have changed.
Due to Nokia's decision to back away from freedom and open source I was forced over the past year or so to rely on a two device strategy while traveling as there were two crucial applications missing for me on Android so far: A decent camera and offline maps + navigation functionality. While the camera issue has improved significantly in the past year I was still hanging on to Nokia Maps and its offline capabilities as Android's Google maps was just too expensive to use abroad and leaked too much of my location information to Google. But now, things have changed.
Open Street maps has come a long way over the years and Open Street Maps for Android (OSMAND) has developed beyond my wildest hopes and now offers car navigation on Android with downloadable maps that worked just great during my recent car trips between Germany, the Czech Republic and Austria. Car navigation worked well, there's a lane assistant that even Google maps does not have and it's ultra configurable to show or hide many details one can be interested in or not. Finding and address is quick, the routes calculated are good, the lane assistant worked.
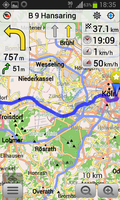 The only two major downsides I came across was that while it perfectly calculated a route between Austria and Germany it wouldn't come up with a route for my trip between the Czech Republic and Austria so I had to split that particular route in two parts. Also, while route calculation for short tips is quick, trips of several hundred kilometers take a bit to calculate, I estimate it to be in the order of 30 seconds. Nokia maps does better in this regard. Like Google maps, Osmand also stops navigating in tunnels when the GPS signal is not present. This is better in Nokia maps which continues to show the route based on a speed estimation. One thing neither Osmand nor Nokia maps in offline mode can do is to show the current traffic situation which is a strong point of Google maps. Having said this, I feel that those drawbacks are a small price to pay for getting an open source solution that doesn't transmit location information to some big web company.
The only two major downsides I came across was that while it perfectly calculated a route between Austria and Germany it wouldn't come up with a route for my trip between the Czech Republic and Austria so I had to split that particular route in two parts. Also, while route calculation for short tips is quick, trips of several hundred kilometers take a bit to calculate, I estimate it to be in the order of 30 seconds. Nokia maps does better in this regard. Like Google maps, Osmand also stops navigating in tunnels when the GPS signal is not present. This is better in Nokia maps which continues to show the route based on a speed estimation. One thing neither Osmand nor Nokia maps in offline mode can do is to show the current traffic situation which is a strong point of Google maps. Having said this, I feel that those drawbacks are a small price to pay for getting an open source solution that doesn't transmit location information to some big web company.
The screenshots on the left show how Osmand looks in practice and I was more than happy to pay the six Euros for the full version to be able to download more than four maps for offline use. So while I had my old Nokia phone as a backup with me on my current trips I didn't use it a single time once I figured out how well Osmand works. From now on I guess it will remain in the cabinet.
Kudos to the OSM and Osmand team and all people contributing to the open maps, this is really incredible!
Chip GSM, UMTS and LTE Network Test 2013 in Germany
Everyday is groundhog day (in case you know the movie) and every year at around the same time, very detailed network tests of German computer magazines give an interesting insight and comparison of the capabilities of mobile networks in practice.
The latest report is from 'Chip' and the top speed they've measured in an LTE network is almost 80 Mbit/s. While this is an exception rather than the norm, other values are equally stunning. Here's a link to the magazines report in German and here in English, thanks to Google translate. Enjoy!
If you are aware of similar reports about networks in other countries, please leave a comment, I'd be quite interested.
A Skype Video Call at 5 MBit/s
While many users have fast DSL lines at home when it comes to the downlink, uplink speeds are typically still very limited. While many might argue that unless you run servers at home (which I do, e.g. Owncloud, Selfoss, Prosody…) this is hardly noticeable I have to disagree now that I have seen how a Skype video call looks like when both sides of the connection have an uplink that allows them to transmit at faster than 1 Mbit/s. The video resolution, quality and frame refresh rate are as stunning as the bandwidth taken once Skype notices what the network can provide. Quite a number of my video calls these days now stream at an uplink/downlink aggregate of 5 Mbit/s. In othr words such video calls consume 2.25 GB of data per hour. Compare that full two hour movies in SD quality I download from my online video recorder that have a mere 1.5 GB per file.
Raising the Shields – Part 8: Prosody – My Own Instant Messaging Server For Family Communication
The next step in raising my shields against all sorts of three letter agencies spying on my data packets on the Internet has been to think about how I can protect myself better against spying on my instant messaging communication between my family members. In part one of this series I've already made the first and most important step by installing "Off The Record" (OTR), an end to end encryption for all sorts of instant messaging services. The server behind the service, however, was still property of a public company and hence my data packets were probably still routed half around the world ready for interception and collection of metadata (i.e. who communicates with whom and when). Time to change that as well.
XMPP is the protocol of choice for running your own instant messaging server as it is supported by quite a number of desktop and mobile messaging clients such as Pidgin that I'm already using. On the network side, one can choose from a number of different solutions and after looking around a bit I chose Prosody. On a Linux based system such as a Raspberry Pi it is straight forward to install as it is included in the software catalog. A "sudo apt-get install prosody", a few changes in the configuration file that are described on Prosody's web page and creating a TCP port forwarding rule in my DSL router was pretty much everything to get it working.
I've been trying it for a week now together with Pidgin and OTR encryption and it works like a charm and the three letter agencies have to work a bit harder now to intercept our family instant messaging traffic to collect metadata. And on the cost side it don't cost me a penny extra as I have the server running together with the Selfoss RSS server (see here and here) that runs on the same Raspberry Pi.
USSD Codes To Speed-Up Android Call Forwarding Activation
 Every now and then I have to sigh when using Android and wished they would have at least implemented telephony features half as intelligent as Symbian did in its days. But gone is gone and I have to make the best out of it. Activation of call forwarding is one such thing I kept sighing about because changing settings requires to go down several menu levels and waiting a couple of seconds for the device to read the current status from the HLR. But now I've found an interesting fix for that: USSD codes.
Every now and then I have to sigh when using Android and wished they would have at least implemented telephony features half as intelligent as Symbian did in its days. But gone is gone and I have to make the best out of it. Activation of call forwarding is one such thing I kept sighing about because changing settings requires to go down several menu levels and waiting a couple of seconds for the device to read the current status from the HLR. But now I've found an interesting fix for that: USSD codes.
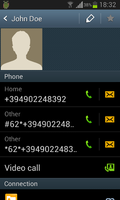
Yes, this 1990's technology to use special command codes in a dial string to interact with the HLR in the network in a standardized way speeds up a 2013 Android device. And here's how it works: As it's usually the same numbers I want to forward my calls to when my device is not reachable one can extend the entry of a person in the contacts by the phone number embedded in the USSD code to perform the desired call forwarding activation / deactivation procedure. The figure on the left shows how this is done for 'call forwarding when not reachable'.
The string starting with the '*' activates call forwarding when not reachable to this number and the entry with '#' at the beginning deactivates it again. Not shown in the image is the '#' sign that follows the phone number. Using the code is then as simple as selecting the entry in the address book and to 'dial' it. There's even feedback that the action has been performed.
Surveillance State: Lavabit, Silent Circle, Groklaw Cease Their Services – Who’s Next?
Three months into Edward Snowden's revelations of PRISM and other government programs to monitor pretty much everything that flows through the Internet today and the news still get worse by the day. Now, first services are shutting down because they can't offer privacy anymore in the bounds of the laws of an open, free and democratic society. Instead they are shutting down because secret court orders they can't even talk about would force them to reveal private information on an unprecedented scale. I find that very disturbing and I feel that we need to speak up against this now as politicans word wide are still not willing to have a public discussion on the right balance between security, privacy and personal freedom.
Don't get me wrong, I am not at all against court sanctioned wiretapping when there is evidence that someone is in the preparation of comitting a serious crime. What I'm against is monitoring everything. Lavabit's owner, Ladar Levinson, who used to run a secure email service that encrytped all data stored on his servers and could only decrypt it while the user was logged in seems to be of the same opinion. Being asked by reporters he stated that in the past he's always complied to court orders to give information out to government agencies on a case by case basis. But it seems the US government now wants to go much further and hence he's decided to shut down the service. Exactly what is going on he can't tell because he is bound to secrecy by law and threatened with imprisonment if he fails to do so. But from the public knowledge how his email service works and his statement that he complied with court orders for surrendering information from and about specific accounts before, it's pretty easy to discern that the latest order went much further, likely a tap for security agencies directly into his system. From a privacy and civil liberty point of view that's absolutely not acceptable.
Next in line was Silent Circle, another secure email provider, who shut down their email service without any notice because it suffers from the same shortcoming: There's no end to end encryption in email as per design. No matter how secure you make transmission, at some point it always has to be encrypted before transmission or storage. And finally Groklaw, a popular law website has shut down as the owner feared that the privacy and confidentiality of her sources was no longer ensured with the current practice of security agencies monitoring the whole Internet rather than only the traffic of persons for which they have a court order for surveillance.
All of these services could shut down because they are privately owned. That of course does not shed good light on the big service providers who have not spoken out against this and keep running their services without being able or wanting to tell their customers of how their private communication is monitored. Society needs trust in order to function. Where's the trust in this? This makes me wonder about the future of Internet companies in the US!? The current state of affairs simply means that it's impossible for customers to trust US companies or US owned companies abroad to securely and privatly handle their data. Secret court orders can force them to reveal sensitive data to governments and what is once out of their hands can then be easily used by governments for many purposes. If I owned a non-US company today the last thing I would do is to store or process any data I didn't encrypt on my own premisis on servers of such companies. Money's usually a strong argument and loosing business because of
run-away anti-terror laws is perhaps a strong incentive to pressure for
change. But trust is lost and it will take a lot to restore it. So perhaps we'll see an Exodus of tech companies from a country to which in the past people fled to because they wanted freedom. It would be ironic in the extreme.
Sure I'm trying everything to better protect my privacy. Those of you who follow my ongoing 'Raising the Shields' sequel know that I go far beyond what a normal user can do. But a lot of my communication is still exposed to mass surveillance and some of it always will be. Raising the shields is treating the symptions, it's not the cure. We need governments to clearly define what security agencies are allowed to do, what they are not allowed to do and to communicate that openly. Otherwise, a significant part of our civil liberties will remain lost.
Were There Computer Learning Kits for Teenagers In Your Country?
There's one thing I have been wondering about while enjoying my recent trips back in time to the 1980's and computer learning kits: Were there similar kits in other countries around the globe tailored for teaching teenagers how computers work (vs. how to work with computers)?
In German speaking countries there were three different kits (Philips 6400, Busch 2090 and the Kosmos CP1) sold mainly via toy stores (yes!). So I searched the net a bit in the languages I am able to understand if I could find similar kits having been sold in other countries but came up pretty much empty handed. Perhaps this is due to the way I searched and the keywords I used but it's difficult to believe this was only something that happened in a few German speaking countries in Europe.
As many of you must have also grown up in the 1980's perhaps you still remember something that could point me in the right direction. If so, please consider leaving a comment!
How To Assign Special Characters To Keys In Ubuntu and Linux
Having friends and business partners around the world I frequently type texts in different languages and so far always struggled with non-standard Roman characters on my German keyboard. At some point I was so fed up that I spent a couple of hours to find a solution to make the process a bit less cumbersome.
While some non-standard Roman characters can be typed even on an German keyboard by using an "accent" modifier key, others such as for example the
'ç' are not directly reachable this way. As I need such characters quite frequently, however, I was looking for a possibility to assign such special characters to standard Roman alphabet keys together with the ALT or ALT-GR modifier key. The 'ç' for example should be reachable with the ALT or ALT-GR key (not available on a standard US keyboard) + the standard 'c' key.
On Ubuntu and I guess many other Linux based GUI's, the ALT key is already used for other purposes by the GUI so I focused on a solution with the ALT-GR key. As this key is not available on the standard US keyboard layout I am not sure if the following also works for this keyboard layout. But for all layouts that have an ALT-GR key here's the command to put the 'ç' on ALT-GR + c:
xmodmap -e "keycode 54 = c C c C ccedilla Ccedilla ccedilla Ccedilla"
54 is the code for the key on which the standard Roman "c" is located at on a German keyboard.
The current assignment of all keys is queried with the following command:
xmodmap -pk
and
xmodmap -pk | grep "(c)"
with the brackets around the character filters the output for the line with the code for key to which a specific character is assigned.
Non-standard Roman characters have a name that can be used in the assignment command above. The 'ç' character, for example like in 'François', is called ccedilla for the lowercase variant and Ccedilla for the uppercase variant. For the list of other special characters have a look here.
For each special character assignment a separate xmodmap -e… command is required. Changes are not persistent, however, i.e. a reboot returns the computer to the standard keyboard layout. To make the assignments persistent one can for example put all xmodmap commands in a shell script and execute it automatically during the login process.