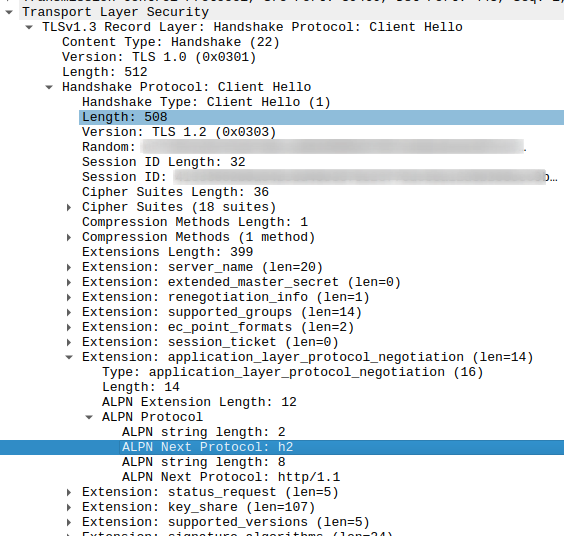
When 3GPP set out to define the 5G core network (5GC), it used all the latest and greatest web technologies to radically reshape core network architecture. One tiny part of this is the use of HTTP/2 for signaling between functions. This made me wonder just how on the Internet today, web browsers and servers decide if HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2 is used for communication. Yes, I went off a bit on a tangent there. It can’t be the TCP port, as port 443 is used with both protocols for encrypted connections. So there must be something else.
Continue reading HTTP/2 in the 5G Core – How Does that Work In the Web Today?Things That Moved Me in 2020 – Part 2
And off we go with part two with a summary of things ‘that moved me’ in 2020. Apart from the wireless network related topics I wrote about in part 1, the year 2020 was certainly the year video conferencing had a breakthrough for many people. As I value my privacy I was not really keen to have all my meetings over infrastructure and software provided by large 3rd party companies that use closed source software and don’t give much about privacy and confidentiality. So I set up my first open source Jitsi video conferencing server in a German data center for private conversations and meetings. Much easier than I thought! I then gave a talk about it at DiVOC (‘Digital verteiltes Online Chaos’), the first conference gone online in the year 2020 I attended and was run-over by interested people. And from there, things escalated quickly.
Continue reading Things That Moved Me in 2020 – Part 2Things That Moved Me In 2020
There must be few people on this planet that have not been affected by the Covid-19 pandemic this year. It has certainly brought profound changes in my way of working and in the things I did this year. So while the pandemic restricted me to stay at home most of the time, it ‘moved me a lot’ in other ways, which is I why I had to start my annual ‘Things That Moved Me’ post for 2020 with this topic. As always I can hardly believe that another year has passed again already, so let’s dive into it:
Continue reading Things That Moved Me In 2020SSD, ZFS and VM performance – Workstation Power At Home – Part 12
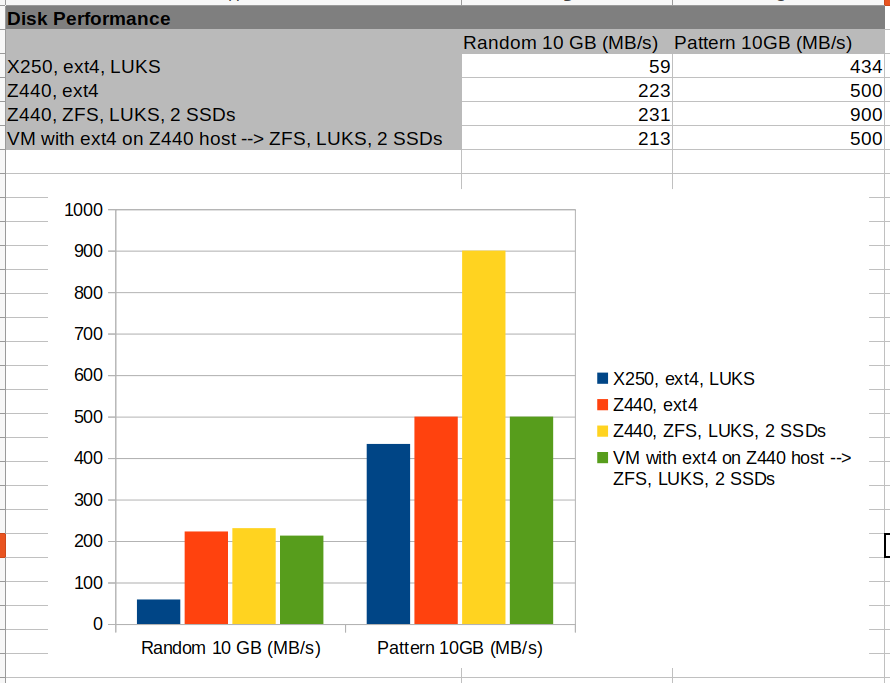
Now that I have my ZFS filesystem spanning several drives in place on my Z440, I wanted to get an idea of how this setup is performing together with the underlying LUKS encryption. And while I am at it, the other questions I had in mind were: How does this compare to the ext4/LUKS combination I use on my notebook and how does the write performance look like from inside a virtual machine running on my Z440. A lot of obvious results but also quite a number of surprises.
Continue reading SSD, ZFS and VM performance – Workstation Power At Home – Part 12ZFS with LUKS – Workstation Power At Home – Part 11
This is a quick follow-up post to the previous one in which I’ve written about how straight forward it is to use ZFS to combine several physical SSDs or disk drives to use the combined capacity for a file system. The one thing I left out in the description was how to encrypt the setup. While ZFS encryption is said to have a good performance starting with version 0.8.4, Ubuntu 20.04 I use at the time of writing is still using 0.8.3. The advice of ‘the Internet’ is thus to use LUKS as an encryption layer below ZFS.
Continue reading ZFS with LUKS – Workstation Power At Home – Part 11ZFS for Storage – A Primer – Workstation Power At Home – Part 10
In previous parts of this series I’ve been looking at CPU power, GPU power, virtualization, remote graphical GUIs and networking of my refurbished Z440 workstation. The next thing on my list of things I wanted to improve in my computing setup was storage.
So far, I was mostly using ext4 filesystems on partitions on physical disks. This has served me well over many years, it’s a straight forward approach and disk drives were usually bigger than the amount of space I required. On the workstation, however, this would have been limiting as I had two spare 2 TB SSDs that I wanted to combine to get a filesystem on which I could store up to 4 TB of data. Also, I wanted to have the possibility to extend this later. I discounted spinning disks with much higher capacity (for the moment), which could also have solved my storage problem, as the workstation is below the desk and I wanted to have a quiet system.
Continue reading ZFS for Storage – A Primer – Workstation Power At Home – Part 102.5GbE Performance Revisited – Workstation Power At Home – Part 9
After the both good and bad performance of my Lenovo X250 and Ubuntu 20.04 over a 2.5GbE link to my workstation, I couldn’t just leave the topic but had to further investigate how I could potentially improve throughput when using Ubuntu’s Nautilus file manager to transfer files to and from the workstation. And again, some surprises waited for me.
Continue reading 2.5GbE Performance Revisited – Workstation Power At Home – Part 9
2.5GbE Network Performance – Workstation Power at Home – Part 8
I’m quite amazed I am already into part 8 in this series of exploring the limits of using a headless workstation as a ‘power booster’ next to my notebook. The next thing I have taken a closer look at is the connection between the notebook and the workstation, a 1 Gbit/s Ethernet link. That’s good enough for just about anything I want to do except when transferring large files. And mind you, when I say large, I don’t mean a couple of 100 MBs or even a gigabyte, that just works fine over such a link. But when transferring, say 100 GB, it does become a bottleneck. So something faster is necessary. How hard can it be, I thought, and was quite surprised by the answer.
Continue reading 2.5GbE Network Performance – Workstation Power at Home – Part 8
5G and My Headless Workstation
It’s a bit of a strange headline perhaps but my recent blog posts on working with a headless workstation that supplies extra CPU muscle to my working setup has a lot to do with the envisaged 5G evolution of wireless networks and services. Let me explain…
Remote Visual Computing – Remote X over SSH – Workstation Power At Home – Part 7
In two previous posts I wrote about how to use RDP and VNC to access the graphical desktops of the virtual machines on my headless workstation. Both have in common that the desktop of the remote virtual machine is put into a window on my client machine. That is great for many purposes and when used at the resolution of the screen connected to my client machine in full screen mode, it is almost like working directly on that machine. Also, the whole desktop with all applications running on it can just be ‘minimized’ to the dock when not needed for a while. For Linux virtual machines, there’s a third option that is even cooler for some use cases: Remote X over SSH!
Continue reading Remote Visual Computing – Remote X over SSH – Workstation Power At Home – Part 7